
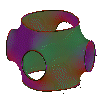
Schwarz's P-surface and deformation (Hermann Amandus Schwarz)
In the most symmetrical case the fundamental domain of translation is
tessellated by 96 congruent triangular pieces of surface.
Such a pieces is bounded by one straight and two planar lines.
In this case the boundary of the fundamental domain of translation
lies on the surface of a cube. As a first deformation one can bend the
surface in such a way, that the boundary of the fundamental domain
of translation lies on the surface of a rectangular solid
which contains two squares.
This one-parameter family is implemented in this library.
As a second deformation you get a fundamental
domain which lies in any rectangular parallelepipedon.
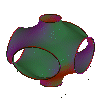

How do I get the complete fundamental domain of translation
when using GRAPE?
The input file name of these surfaces is schwarz.am.
You have to carry out five operations of reflection.
First reflect along the straight line. Then reflect along one of the horizontal
planar lines. At least reflect three times along a vertical boundary line.
 Return to the surface list.
Return to the surface list.
 Return to the project list.
Return to the project list.
 Go back to the main menu.
Go back to the main menu.
grape@iam.uni-bonn.de




 Return to the surface list.
Return to the surface list.
 Return to the project list.
Return to the project list.
 Go back to the main menu.
Go back to the main menu.